LED Light Bulbs vs. The Alternatives
When it comes to choosing the right light bulb, knowing the differences between them can guide your buying decision. This blog will compare LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) to traditional light bulbs. Most traditional bulbs include CFLs, Halogens, and Incandescent bulbs.
To learn more about the different color temperatures of the bulbs, check out our color temperature guide!

Power:
Different bulb types vary in power, this is measured in wattage. The higher the wattage, the more energy the bulb uses to emit light. The image below is a graph of watts it takes to produce specific lumens for a bulb.
Recommended Products
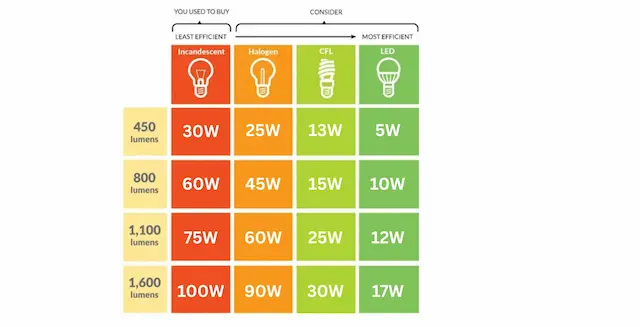
Incandescent vs Fluorescent vs LED
Notice in the chart above that incandescent light bulbs generally have a wattage between 40 and 100 watts. This means incandescent bulbs use a lot of energy to emit light.
In comparison, fluorescent and LEDs have lower energy levels to emit the same amount of light. For example, LEDs use about 90% less energy to power each light bulb than equivalent incandescent lamps.
Halogen vs LED
Halogen light bulbs tend to have wattages between 29 and 72. While halogen lamps are more energy efficient than incandescent lights, they are still not as efficient as LEDs.
When purchasing light bulbs, consider a more energy efficient light bulb. LEDs are the most energy efficient bulb and have reduced significantly in price as technology improved. The longer lifespan and lower energy bills month-to-month offset the slightly higher initial cost of LEDs.
More Energy = More Money!
.jpg&w=390&q=75)
Brightness:
Bulbs can vary in terms of their visible light output. A light bulb’s brightness is measured in lumens. The higher the lumen, the brighter the light will be. To measure the efficiency of a light bulb, it’s most effective to compare brightness (lumens) to power (wattage).
Incandescent vs Fluorescent vs LED Light bulbs
A traditional incandescent bulb emits about 15 lumens per watt. So, to reach a brightness of 800 lumens, a standard 60-watt incandescent light bulb will need to be of use.
CFLs or fluorescent light bulbs emit 60 lumens per watt. To reach a brightness of 800 lumens, a standard 15-watt CFL light bulb will be the bulb of choice.
LED's, however, are the most effective light source, with a whopping 72 lumens per watt. This means that for around 10 watts of power, an LED will be just as bright as a 60-watt incandescent bulb.

Heat Emission:
Did you know that about 90% of the energy from incandescent light bulbs is wasted as heat? Not only do LED light bulbs generate less heat, but they use less power in doing so. Although most electronic devices produce heat, LED light bulbs emit lower temperatures than incandescent and fluorescent light bulbs.
They do this through their fins. Fins are a surface feature that allow the heat to disperse from the base of the light bulb. Traditional incandescent light bulbs do not have this feature. Therefore, after only a few minutes of being turned on, an incandescent bulb is too hot to touch.
LED light bulbs, on the other hand, can remain cool after hours of being on. Learn More about the Thermal Components of LED’s.

Lifespan:
Light bulbs can also vary in lifespan. LED technology has taken energy-efficiency to the next level, with their ability to last up to 25,000 hours. That is 34 years of never having to change a light bulb.
Traditional light bulbs, like incandescent light bulbs have a lifespan of about 1.4 years, or 1000 hours. Halogen Light bulbs can last up to 4.2 years, and CFL’s can last up to 14 years. Read our blog on Converting Lifespan Hours to Years.

Mercury
Unlike popular compact fluorescent light bulbs, LED’s do not contain small amounts of mercury. In the case that a fluorescent bulb breaks exposing the mercury gas, it could cause potential harm to those close to it.
Mercury can pose a great threat to young children and can spread to other parts of the building. Because LED’s do not contain mercury or any other toxic chemicals, they do not spread hazardous waste when they are broken. LEDs are a more environmentally friendly and safer choice.

Annual Cost of Operation:
Let’s say you are currently using 20 incandescent light bulbs at 60 watts to light a small commercial building, for an average of 12 hours a day. This is considering that the lights are to remain on for a full 12 hours. To find the annual cost of operation, you will need to know the equation for future references.

Annual cost of operation based on 800 lumens for 2 hours per day at $0.16 per kWh
Calculating Annual Cost of Operation
- 60 Watts = 0.06 kilowatts (kW)
- 0.06 kW x 20 light bulbs = 1.2 kW
- 1.2 kW x 12 hours/day = 14.4 kWh per day
- 14/4 kWh/day x 365 days = 5,256 kWh per year
- 5,256 kWh/year x $0.16/kWh = $840.96
As seen above, using incandescent lights is an expensive option year round. The chart below shows the cost per year and the potential savings for each bulb compared to the incandescent.
| Bulb Type | Cost per Year | Savings/Year (compared to incandescent) |
| Incandescent | $840.96 | - |
| Halogen | $605.49 | $235.47 |
| CFL | $210.24 | $620.72 |
| LED | $142.96 | $698.00 |
Did you know that...
ENERGY STAR offers rebates and tax incentives when you make energy-efficient lighting improvements. Learn More!
Recommended Reading
Outdoor lighting costs commercial facilities a lot of unnecessary energy expenses. Use LED wall pack lights to increase efficiency in both cost and lighting performance.
The role of UV LED light protection is important for maintaining skin and eye health. Read more about UV LED lighting safety, risk factors, and how to use it responsibly.
Reducing the amount of energy you use in your home can help you save money and decrease your carbon footprint! With a few simple changes, like switching to LED lighting, unplugging electronics when you're not using them, and a few more, you can reduce energy consumption.
Make sure to disconnect the power before starting. Stay safe during LED tube retrofitting!
Recommended Products
Receive special deals and more, right to your inbox
Receive special deals and more, right to your inbox






.jpg&w=500&q=75)


