Shunted vs Unshunted Tombstone Sockets
Shunted vs Unshunted Tombstone Socket
What is a tombstone socket?
The term "tombstone" refers to the shape of the socket that provides a track from the ballast to the lamp's pins.
Tombstone sockets usually go by names like tombstone light socket, fixed socket tombstone, or simply socket.
Their shape, an upright rectangle with slots, helps them to move electricity smoothly from the ballast to the lamp's pins. This design contributes to the efficient linking of the lamp by ensuring a reliable flow of power.
Shunted vs Non Shunted
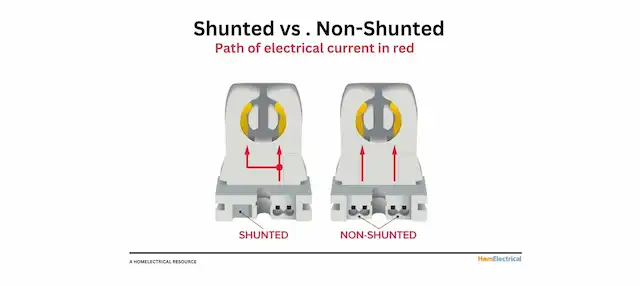
Shunted Socket - Shunted tombstones have a single track for electrical current flow.
Non-Shunted Socket - Non-Shunted tombstones have two tracks for electrical current to flow through independently
What is shunted tombstones?
Shunted tombstones have a single track for electrical current flow. This design creates a seamless path from the ballast to the lamp's pins.
Shunted sockets utilize a single set of wires to receive voltage. They transfer this power to two contacts. This makes them well-suited for specific 'fluorescent tubes' and 'fluorescent fixtures.'
In simpler terms, the contacts inside a shunted socket always link. This constant linking helps shunted tombstones provide a straightforward path for electricity.
What is non-shunted tombstones?
Unlike shunted sockets, non-shunted sockets (or unshunted lamp holders), two paths of electricity flow instead of one continuous path. Unshunted sockets do not use internal connects like shunted tombstones do.
Non-shunted sockets are not connected electrical contacts. In other words, they operate on a two-point flow into two-pin contact.
This characteristic provides more room to adjust how the current flows between the two contacts. It offers flexibility for various retrofitting projects. In non-shunted sockets, you can use tools like a voltage meter to precisely measure electrical potential.
What is the difference between shunted and non-shunted Socket?
Shunted sockets are "connected" or "joined" due to their connected internal electrical contacts. This means that electric current travel along a single path from ballast, down the socket, through to the lamp pins
Non-shunted sockets use separate contacts, or entry points, for wiring. This method creates two separate tracks that electric current travels through. Therefore, non-shunted tombstones are not "connected" like shunted tombstones are.
When to replace a tombstone socket
To check if you need to replace the existing tombstones, visually inspect the shunted or non-shunted sockets. Make a note of specific details such as the presence of a ballast and the arrangement of L/N wires. Additionally, check for any maintenance stickers during the inspection. These details are crucial for evaluating the condition and type of sockets in use.
By thoroughly examining these elements during the inspection, you can make informed decisions about whether to replace the tombstones.
However, visual inspection may not clearly determine socket type.
For accurate identification, use a voltage meter set to "continuity" to test metal contacts in the sockets. A beep indicates positive continuity and a shunted tombstone, while no continuity suggests a non-shunted tombstone.
What type of socket do I need?
Ensuring the appropriate socket for your linear fluorescent or LED light fixture is crucial for many reasons. Selecting the right socket maximizes the lifespan of your lighting system and prevents issues in the future. Issues such as lamp failure or electrical short can pose a fire hazard.
Using the wrong tombstone may even void the UL listing or warranty on the lamp. Therefore, choosing the correct socket is imperative to maintain the safety and longevity of your lighting setup.
It is important to know whether you need to bypass the ballast or remove the ballast completely. Also consider that requirements for fluorescent lights and led tubes can be different. Using the same socket for a fluorescent tube for an LED tube could lead to an electrical short.
Read the manufacturer's recommendations when purchasing ballasts or lamps to check compatibility.
In general, socket pairings follow general guidelines below, however, there are always exceptions:
- T5 (Dimming Ballast Rapid or Programmed-start Ballast): Unshunted socket
- T5 (Instant-start Ballast): Shunted
- LED T5 (Plug & Play): Shunted
- T8 (Dimming Ballast Rapid or Programmed-start Ballast): Unshunted
- T8 (Instant-start Ballast): Shunted / Unshunted (external shunt)
- LED T8 Plug & Play: Shunted
- T8 (Single-end Direct wire / Ballast Bypass): Unshunted
- T8 (Double-end Direct wire / Ballast Bypass): Compatible with both Shunted and Unshunted
- LED T8 (Remote Driver / Type C): Unshunted
- T12: Non-shunted
Recommended Reading
Often seen on fluorescent bulbs, tombstones, or sockets, provide power to a light bulb. This guide can help explain the difference between shunted and non-shunted tombstones, troubleshooting tips, and when to consider replacing a bulb.
Recommended Products
Receive special deals and more, right to your inbox





